公开课 Computer Architecture
课程网址 虽然标题是Computer Architecture,但这个课程和本科的体系结构课不太一样,主要关注更现代的技术,而不局限于经典的5级流水CPU设计。
1. Pipelining review
经典5级流水线 IF-ID-EX-MEM-WB
ID阶段除了读寄存器外,还会为跳转指令做计算: 比较两个寄存器的值,计算出可能使用的目的地址,容易误以为计算地址在EX阶段。(只是本文的context,实际上在哪一步算由硬件说了算)
Structural Hazards
指硬件冲突,假设只有一个访问memory的硬件,那么 IF 和 MEM 阶段不能同时进行
Data Hazards
DADD R1,R2,R3 # R1 <- R2 + R3
DSUB R4,R1,R5
AND R6,R1,R7
OR R8,R1,R9
XOR R10,R1,R11
上面除了第一条指令外,所有指令都要依赖DADD的R1的值,由于DADD 写入结果到R1要在WB阶段 (CC5),因此DSUB 的 ID阶段 (CC3) 和 AND 的 ID阶段(CC4) 都读不到正确的R1值,需要stall。 OR指令的 ID阶段也在CC5,但读寄存器在 the second half of the cycle,写寄存器在the first half,因此不受影响,XOR更不受影响。
- Forwarding The ALU result from both the EX/MEM and MEM/WB pipeline registers is always fed back to the ALU inputs.
Data Hazards Requiring Stalls: 也有必须要stall的时候,比如
LD R1,0(R2)
DSUB R4,R1,R5
即使有forwarding, LD 指令也只能在 MEM 周期快结束时将值写入ALU input,但DSUB需要在这个周期的前半部分就拿到值做运算,因此还是只能stall。
典型的MIPS程序中,两个跳转指令间大概只有3到6条指令,且这些指令间很有可能有依赖关系,所以能并行执行的空间很小,we must exploit ILP across multiple basic blocks(从头到尾,顺序执行没有任何跳转的代码块).
Data Dependences
An instruction \(j\) is data dependent on instruction \(i\) if either of the following holds:
- Instruction \(i\) produces a result that may be used by instruction \(j\).
- Instruction \(j\) is data dependent on instruction \(k\), and instruction \(k\) is data dependent on instruction \(i\).
A dependence can be overcome in two different ways: (1) maintaining the dependence but avoiding a hazard, and (2) eliminating a dependence by transforming the code.
数据依赖可能发生在寄存器层次,这种很好检测,但如果发生在memory层次就很复杂,比如100(R4) 和 20(R6) 可能指向的是同一个地址。
Name Dependences
A name dependence occurs when two instructions use the same register or memory location, called a name, but there is no flow of data between the instructions associated with that name. There are two types of name dependences between an instruction \(i\) that precedes instruction \(j\) in program order:
- antidependence 指令\(i\)先读一个reg/mem,之后指令 \(j\) 向同一个位置写值,这种前后关系不能改变,否则 \(i\) 会读到错误的值
- output dependence 指令 \(i\) 和指令 \(j\) 写入同一个地址,也需要保证顺序
####
The goal of both our software and hardware techniques is to exploit parallelism by preserving program order only where it affects the outcome of the program.
3种可能的data hazard
- RAW(read after write)
- WAW(write after write) anti-dependency
- WAR(write after read) output-dependency
Control Dependences
在可以保证程序结果正确的前提下,执行当前不应该执行的指令虽然会打破control dependences,但这也是OK的。对程序正确性重要的是exception behavior 和 data flow
Branch Hazards
正常情况下,因为跳转指令要在 ID 阶段结束后才知道目的地址,所以流水线的紧跟的下一条指令需要在本来的 ID 阶段重做一次 IF 以获取正确的地址,相当于 stall 一次。
Reducing Pipeline Branch Penalties
- freeze or flush the pipeline: holding or deleting any instructions after the branch until the branch destination is known.
- predicted-not-taken: 假设每个跳转都不成功,先执行后面的指令。如果算出需要跳转,将后面的指令设置成no-op, 并且从新地址开始执行。因为branch hazard只会影响branch之后的一条指令,所以很容易恢复。
- predicted-taken 在本文的上下文中,因为target address在 ID 之后才知道,所以这个方法没有用,但在其他硬件中可能有用。
- delayed branch 在branch 指令之后插入一条一定会执行的指令,由编译器选择。
DADD R1, R2, R3
if R2 = 0 then
...
那么把DADD指令移动到跳转指令之后
if R2 = 0 then
delay slot: DADD R1, R2, R3
Reducing the Cost of Branches through Prediction
Static Branch Prediction
use profile information collected from earlier runs.
Dynamic Branch Prediction and Branch-Prediction Buffers
使用branch-prediction buffer 记录是否跳转来作为hint,一个跳转地址由两个bit给出提示
11 Taken
10 Taken (but last time is Not taken)
01 Not taken (but last time is taken,因为是从 00 变化来的,防止抖动)
00 Not taken
保证准确的异常顺序
在流水线中,可能第\(i\)条指令在MEM 阶段发生异常,而第\(i +1\) 条指令在IF 阶段就发生异常(page fault),时间上 IF 的异常发生的更早,但我们不能直接进入 IF 的异常处理程序,而是要先处理第 \(i\) 条指令的异常。MIPS实现方式是为每个指令维护一个exception status vector,标记每个流水线阶段是否发生了异常,等到了 WB 阶段,再检查 vector 是否有异常,并选择最早的指令(按 unpipelined 顺序)处理。
Extending the MIPS Pipeline to Handle Multicycle Operations
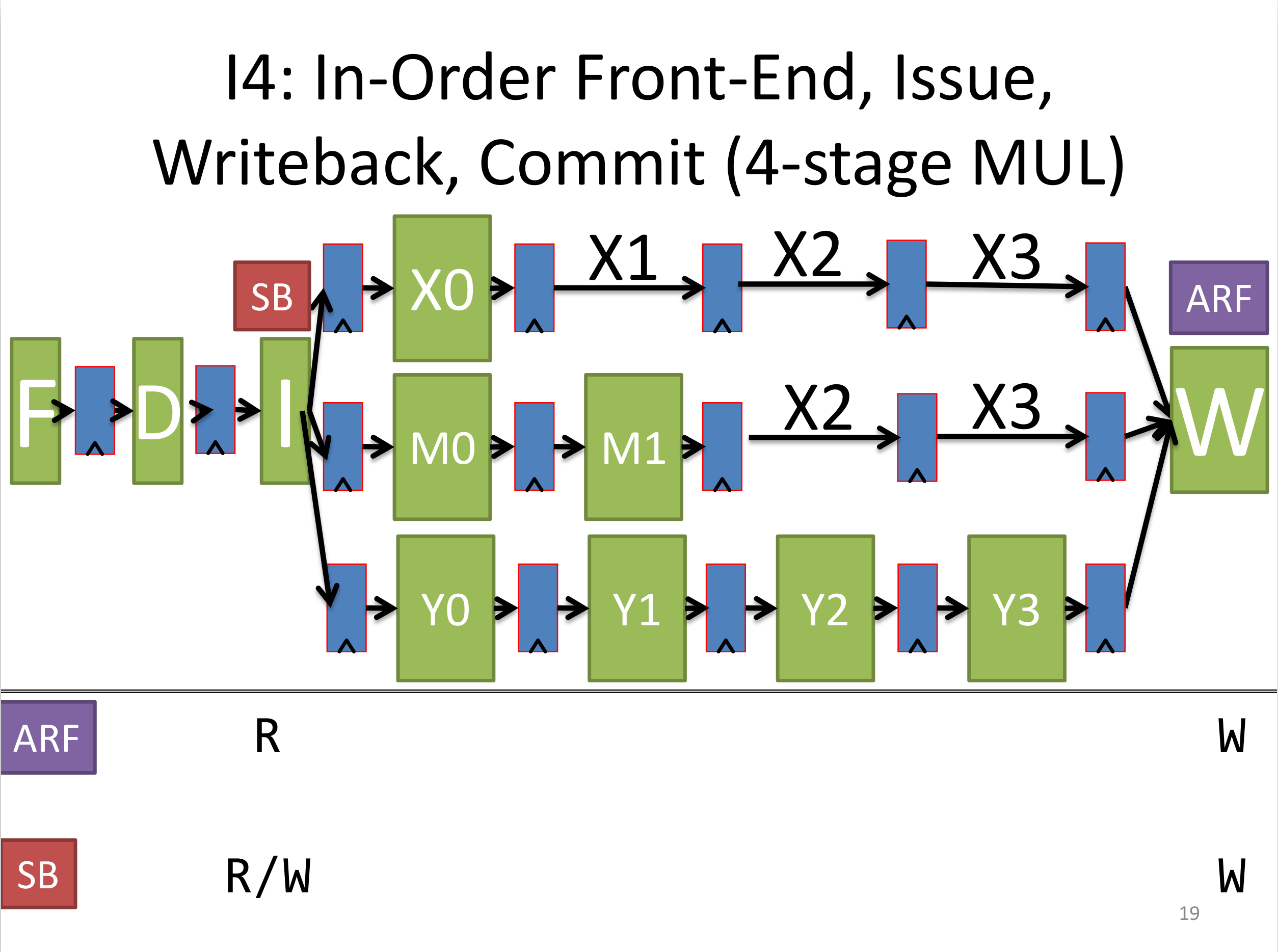
MIPS 浮点数操作不可能做到1个或者2个周期,如果把其想象成整数pipeline,可以认为 EX 阶段需要反复执行多次;其次,有很多FP functional units,由于structural hazard 或 data hazard会造成stall。
这一节中,假设有4套分开的functional units
- The main integer unit that handles loads and stores, integer ALU operations, and branches
- FP and integer multiplier
- FP adder that handles FP add, subtract, and conversion
- FP and integer divider
如果进一步假设这些硬件不是流水线化的,那么一条 float 运算指令就可能在 EX 阶段重复多个周期,它后面的另一条 float 指令也就必须stall。
2. Cache review
3. Superscalar
While a superscalar CPU is typically also pipelined, superscalar and pipelining execution are considered different performance enhancement techniques. The former executes multiple instructions in parallel by using multiple execution units, whereas the latter executes multiple instructions in the same execution unit in parallel by dividing the execution unit into different phases.
superscalar可以是顺序或乱序的,一个简单的顺序 superscalar 结构如下
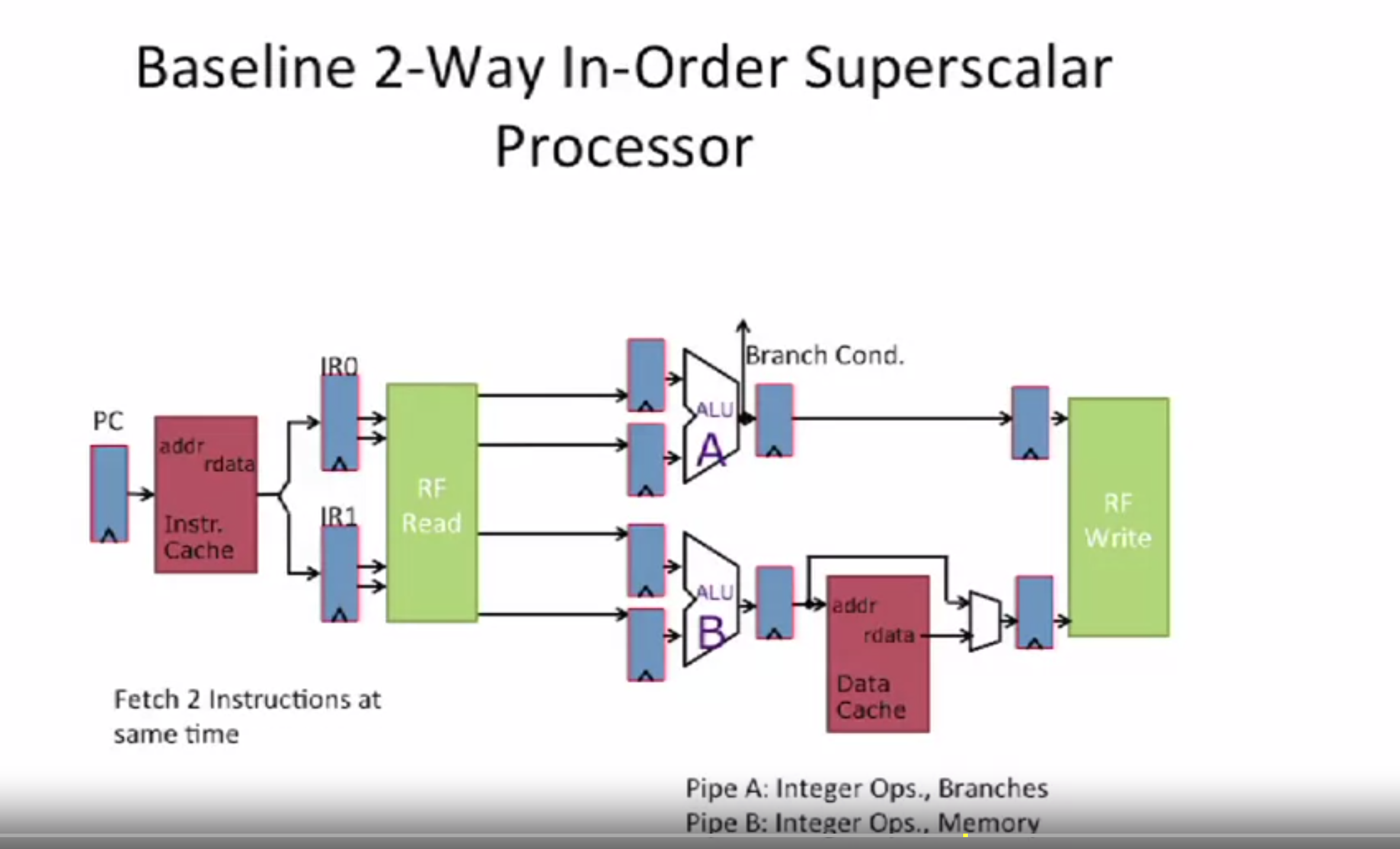
可以看到,有两个ALU,两个pipeline,但只有一个Memory结构, 因此在 ID 阶段需要分配指令到合理的pipeline,比如访问内存的只能去ALU-B.
一个取两个指令,需要考虑cache line 对齐的问题。
CPU乱序执行可以发生在不同的阶段,如下
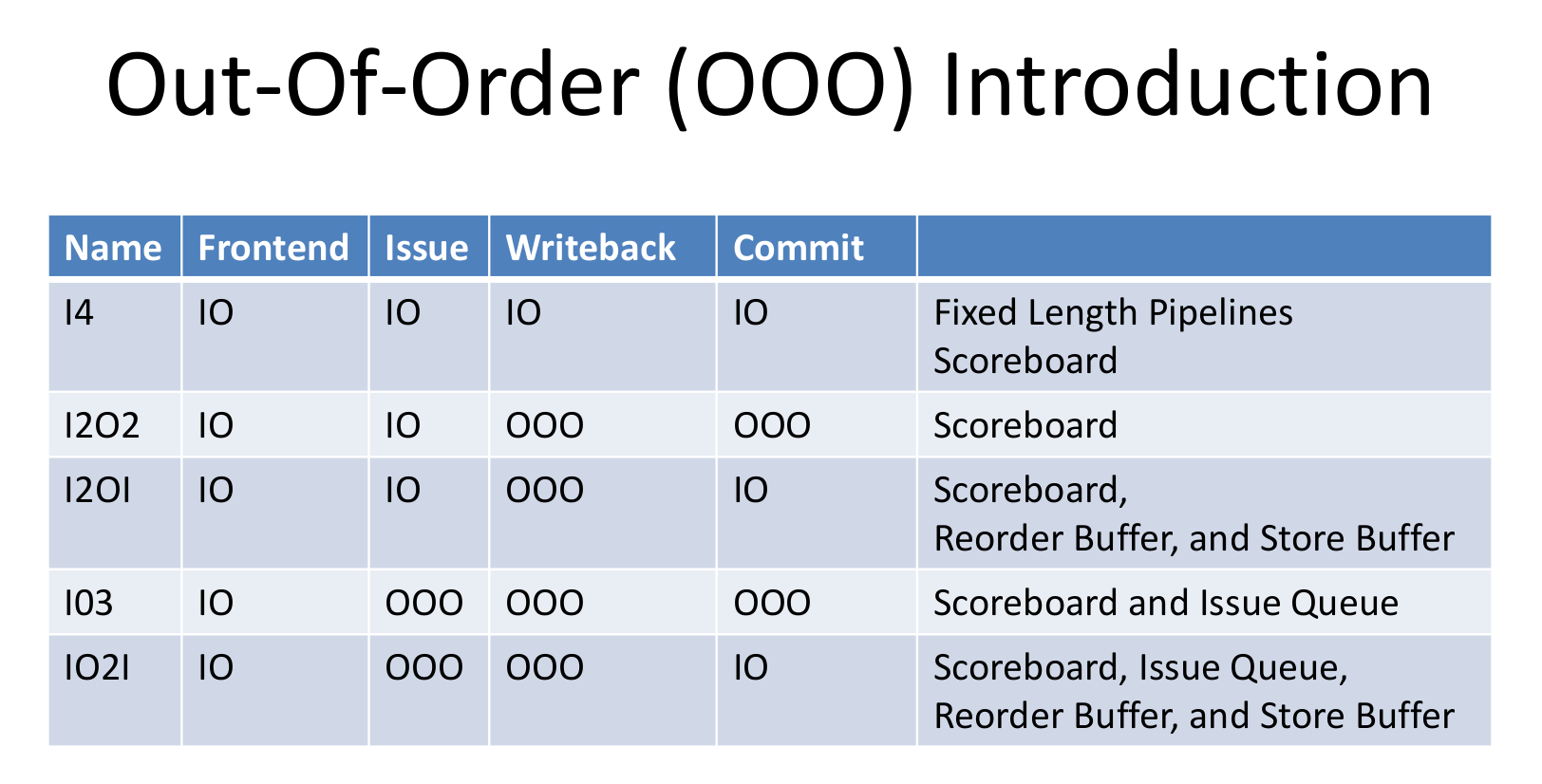
basic scoreboard用来记录当前硬件已经被使用了哪些部分,比如假设指令 \(i\) 会写结果到寄存器 \(r1\) ,那么当指令\(i\) 进入 EX 阶段前就会在scoreboard记录 \(r1\) 被用作output,如果第 \(i + 1\) 条指令也会写结果到 \(r1\) ,就会等待指令 \(i\) 执行完再开始执行。
I4
I2O2
I2O2的结构如下
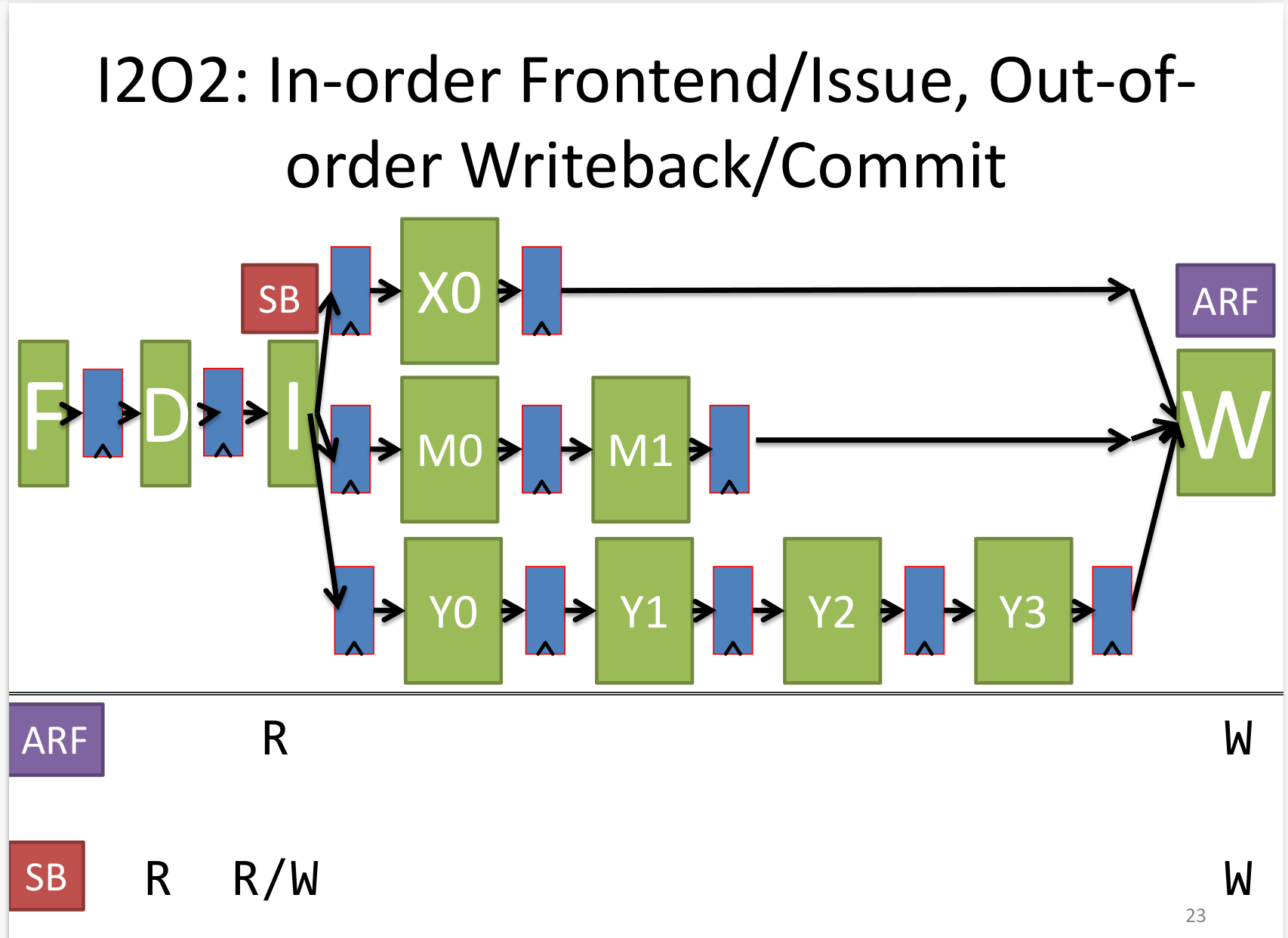
在I2O2结构下,允许后面的指令先完成write back,但是仍然一次只能一个指令写,否则structural hazard。另外,由于write back和commit都是乱序的,要保证precise exception比较麻烦,但也有可能的办法比如将commit point提前几个阶段,这样后续的指令很容易知道前面的指令有没有出现exception。
I2OI
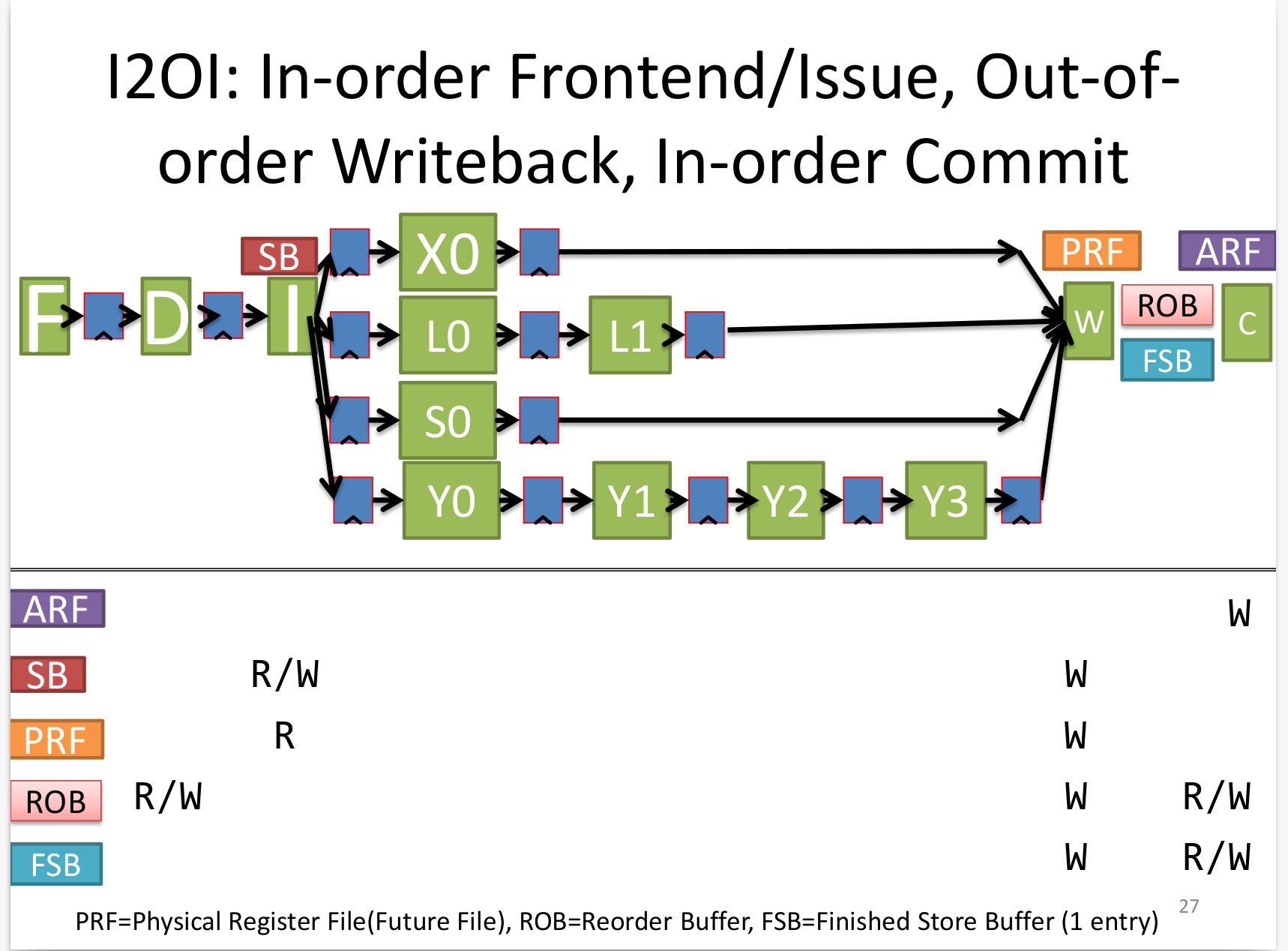
commit in order,可以很好解决precise exception的问题。 上图结构中,Load 和 Store 被分成了两个pipeline, 且 store 会更短一点。
- PRF 保存的值是speculative,遇到exception或branch,可以丢掉。写入PRF的值可以是乱序的。中间结果全部写在PRF
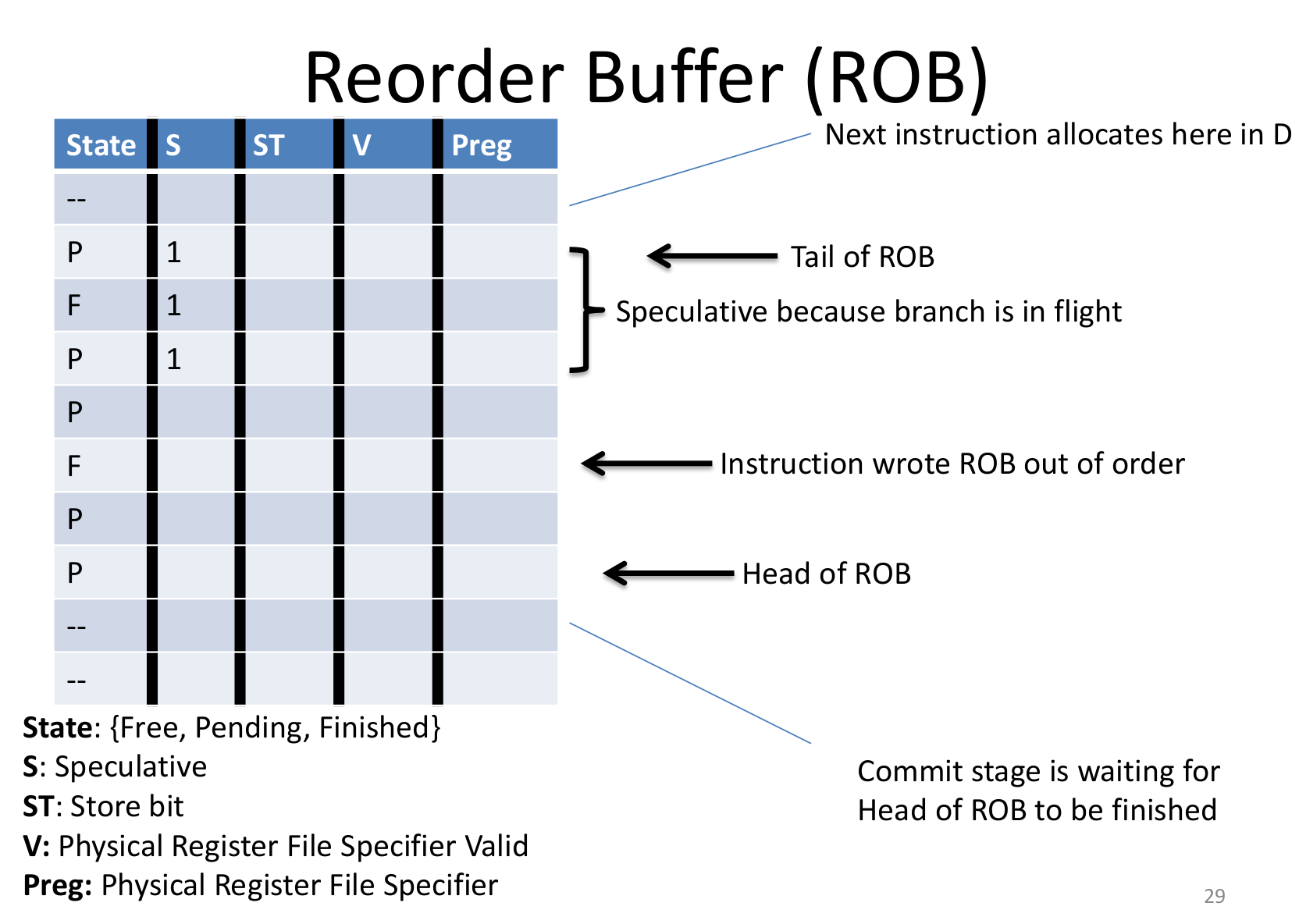
- ROB 虽然 write back 是乱序的,但ROB会让 commit 是顺序的。ROB顺序接收到达的指令,也让这些指令按顺序离开(FIFO)。
- FSB 不想在那么早的阶段执行完 store,因为很难rollback,就先写相关信息到FSB
IO3
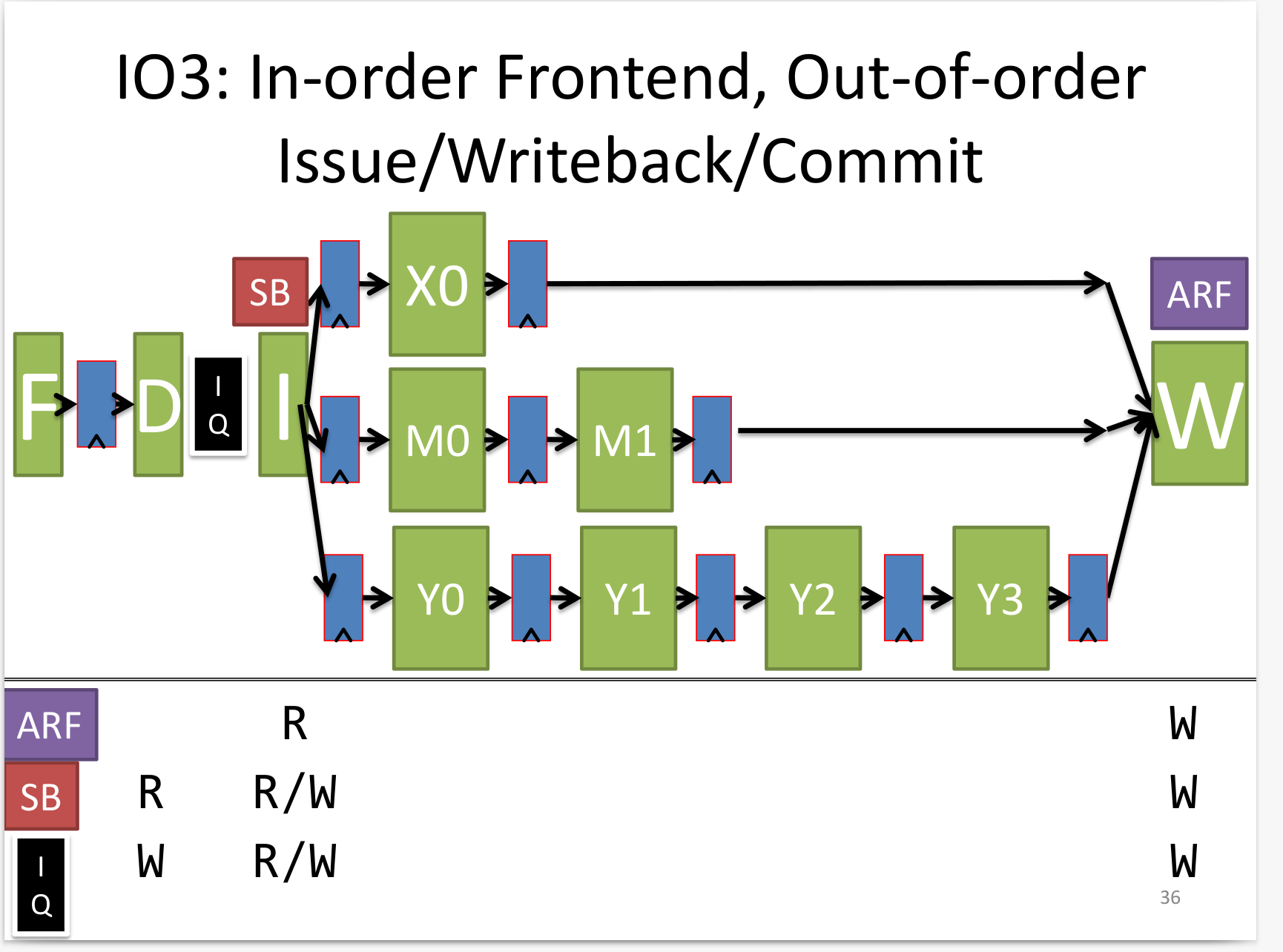
新增一个 IQ(issue queue) 结构,按顺序放入指令到其中,但取出指令是乱序。
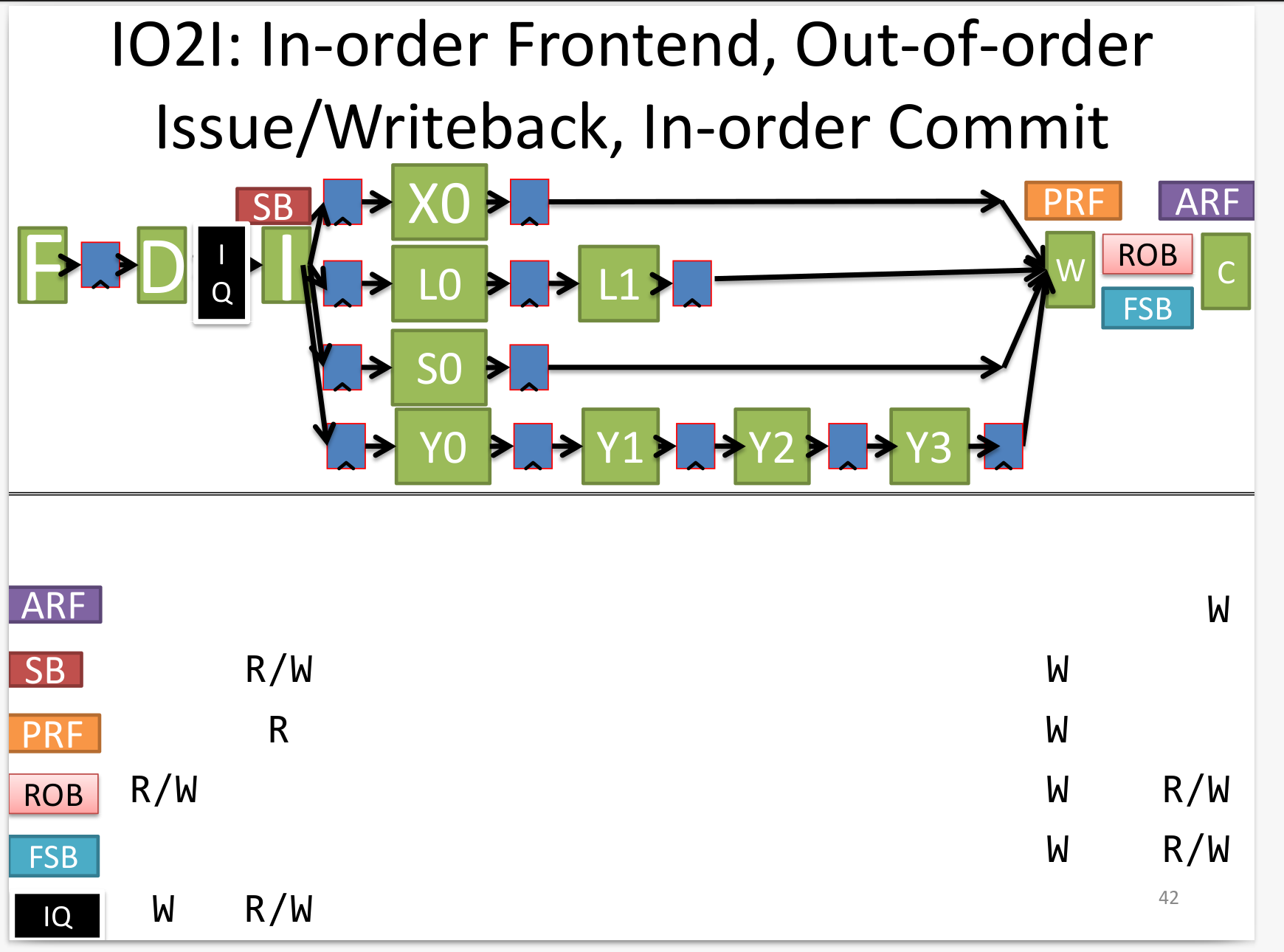
IO2I
Register Renaming
WAW and WAR are not “True” data dependencies, but RAW is.
WAW 和 WAR都可以通过增加寄存器的方式来解决,即写入到另一个寄存器里,就不再有依赖关系。但并不能无限制地增加寄存器,因为寻址空间有限。
Register Renaming with Pointers to IQ and ROB
假设在 IO2I 结构中进行register renaming,需要引入RT(rename table), 记录architectural register 到 physical register的映射。 physical register的数量可以比architectural register的数量多。另外需要引入 free list,记录当前有哪些空闲的physical register可供使用。最后是在reorder buffer中增加3列,architectural register编号,physical register编号以及之前的physical register编号(即当前映射关系之前的最后一次映射关系)。
IO2I结构执行4条指令如下图:
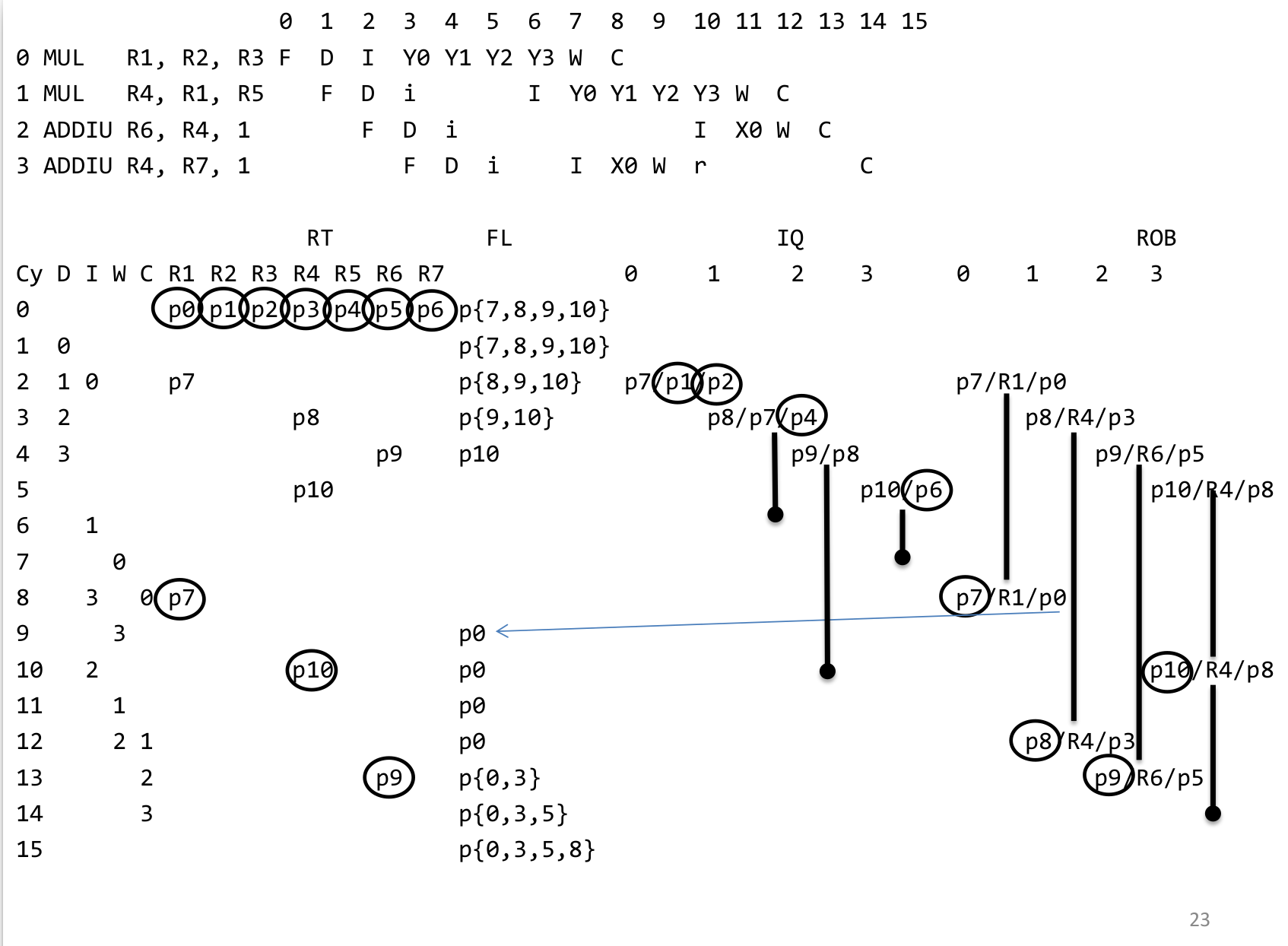
初始时,R1对应p0, R2对应p1…R7对应p6,还有p7, p8, p9, p10 4个physical register没有被使用,被放在free list中。 当每一条指令被fetch后,会为其destination register从 free list中选择一个physical register进行映射,source register则是从renaming table中查询应该读哪个physical register。这样指令中所有的寄存器都被替换成了physical register,且消除了WAW,WAR依赖,因为destination register一定被映射到了新的寄存器中。最后当指令commit后,将destination register之前映射的physical register放回free list中(比如上图周期9),因为之后读destination register都要从映射的physical register读。
Register Renaming with Values in IQ and ROB
仍然是IO2I结构,在reorder buffer保存value而不是pointer,因此没有physical register(因为值已经存在reorder buffer了),也就没有free list。对于issue queue,因为要在执行前知道source的值,因此也会把值存在issue queue的entry里,对于in flight的值,暂时还不知道具体是多少,就存储这个architectural register所在的ROB index。每当有ROB commit一个值到architectural register file,就会广播这个事件,issue queue就能知道值,准备好所有数据后就能issue。 renaming table类似,会告知当前register的值是在architectural register file,还是在ROB中但还没有commit,还是in flight没有被计算出来。
Memory Disambiguation
假设有一条store语句,后面跟一条load语句,考虑这两条语句能否乱序执行。可以引入预测。
4. VLIM
上面的out of order superscalar,需要很大量的逻辑电路来寻找合适的指令进行执行。还有一个缺点是,编译器将一段C代码按某种ordering编译成了一串顺序指令,而processor又要自己在这一段顺序指令中分析出依赖关系,然后并行执行,而这些关系在编译器阶段本来就是已知的,这里两次转换浪费了性能。
VLIM消除了动态调度,让一条指令执行多个操作,比如(add r1, r2, r3; mul r4, r5, r6),指令顺序由编译器指定.
- VLIM需要编译器发现可并行的部分,尤其是面对循环,分支时比较难。
- VLIM 每当切换机器就有可能需要重新编译,即使是同产品线的机器,因为可能有不同的硬件规格。
- VLIM 编译出的代码体积大,需要填充 no-op,或者循环展开
- VLIM比较难实现precise exception
其他关于 VLIM 的讲解(主要是prediction)先略过,因为 VLIM 在通用CPU上不成功了,不是专业人士暂时没有必要深究。
5. Branch Prediction
有些跳转可以在 Decode 阶段确认下一次PC(j),有些则要等到EX (jr)
现代CPU分支预测准确率在95%以上,甚至98% 99%。
static prediction
- backward branch(向已经执行过的指令跳转),有90% 会跳转 (loop),forward branch只有50%
- 在指令中添加1位,由编译器提示是否会跳转
- always Not taken
dynamic prediction
2-bit predictor
Branch History Table(BHT),用branch的PC作为索引,每个entry可以是一个2-bit predictor
Branch History Register(BHR), records the direction of the last N branches executed by the processor(shift register), we can use BHR to index a BHT entry.
two-level branch predictor,BHR index multiple table,use branch PC to choose one.
Generalized Two-Level Branch Predictor,有多个BHR,由branch PC来选用哪一个(97%)
Tournament Predictors: 选择Global/Local predictor
target address prediction
预测跳转的地址。
Branch Target Buffer(BTB)
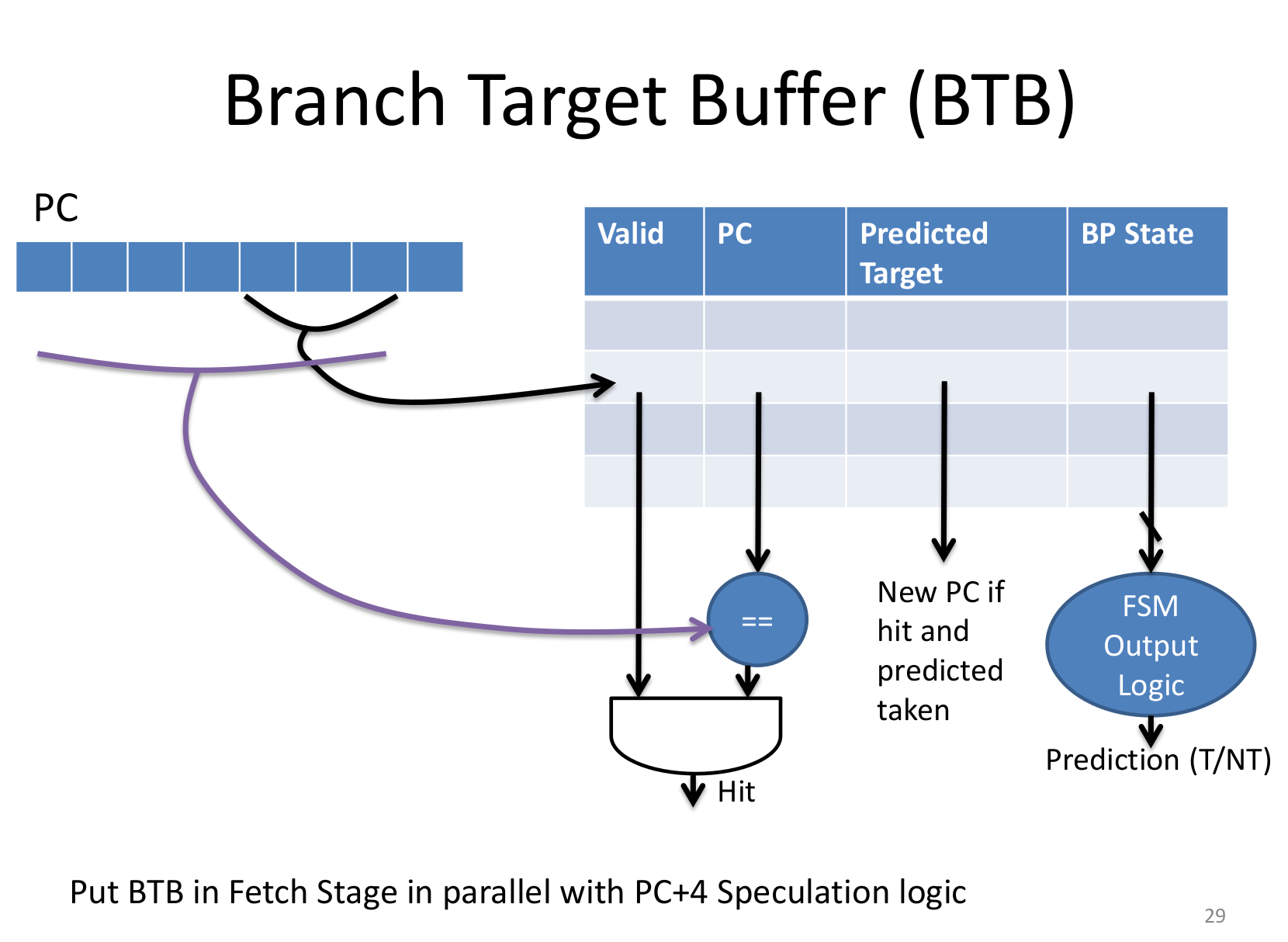
Put BTB in Fetch Stage in parallel with PC+4 Speculation logic
对于函数返回,可以额外记录stack中的return address到某个地方,返回时用作预测的地址
6. Advanced Cache
cache 越小越简单,hit time就越小。
写cache通常需要两个周期,一个check tag,一个写数据。一种解决办法是引入cache pipeline:
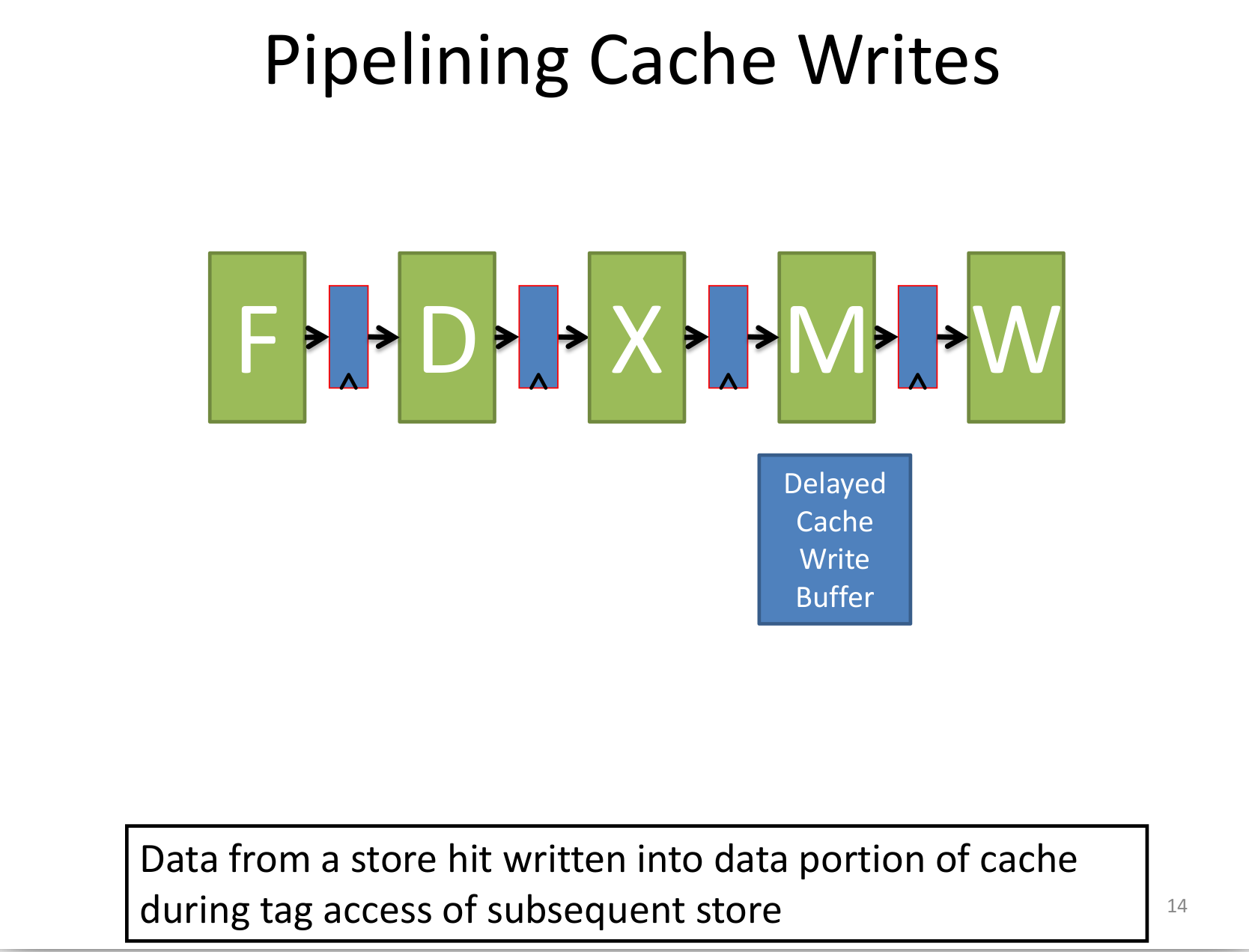
使用L2 cache可以让L1 cache更小更快,也可以让L1 cache从原来的write back变成 write through(且更有利于cache coherence)
- Inclusive cache L1有的数据L2都有
- Exclusive cache swap lines on miss
Victim Cache: Small Fully Associative cache for recently evicted lines. 如果L1 cache 清除一些line,将其放进victim cache,如果L1 cache miss,会尝试从victim cache中找数据。
cache可以引入prefetch,但如果做的不好(提前拿了,但不用)会浪费cache空间和带宽。prefetch怎么做还是看如何设计,没有统一标准。
比如一种硬件指令预取
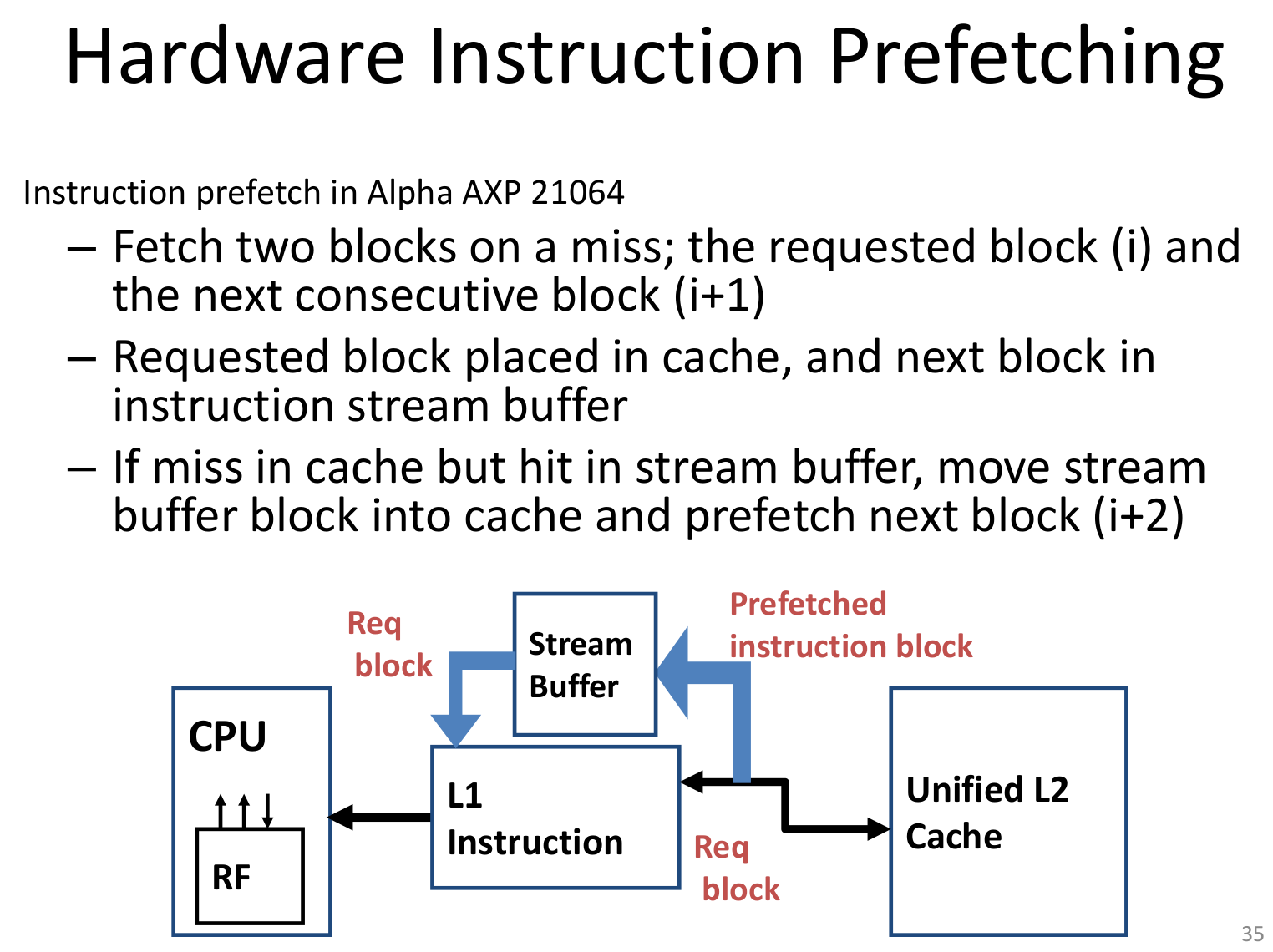
data cache prefetcher预取一个block when access/miss
也可以有software prefetching.
cache multiporting: cache有多个端口,支持two stores to the same line, or load and store to same line,但这样会增大尺寸,且增加hit time。
banked cache:
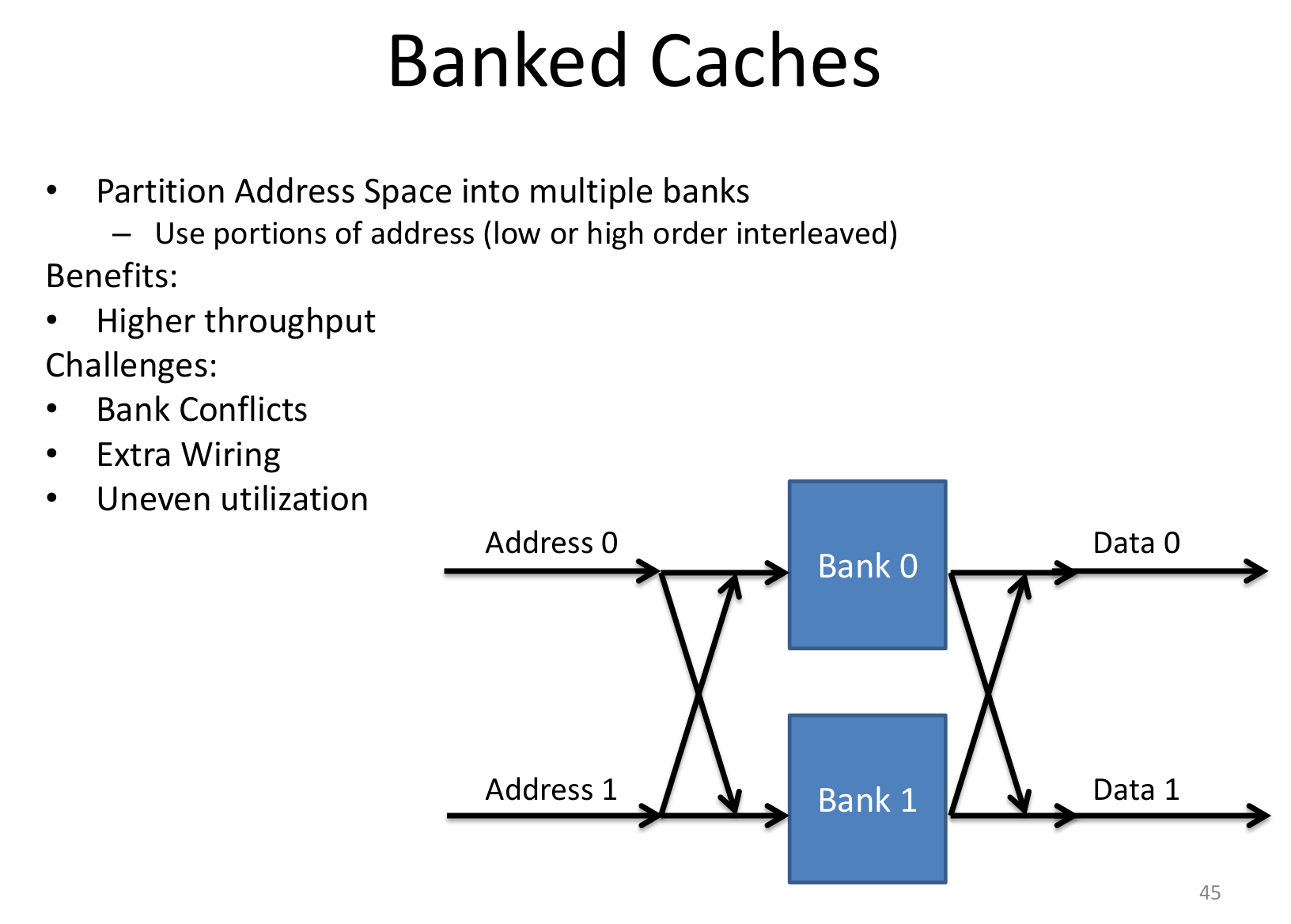
软件优化:
- Restructuring code affects the data block access sequence
- Prevent data from entering the cache
- Kill data that will never be used again(flush/invalid)
loop fusion
non-blocking cache
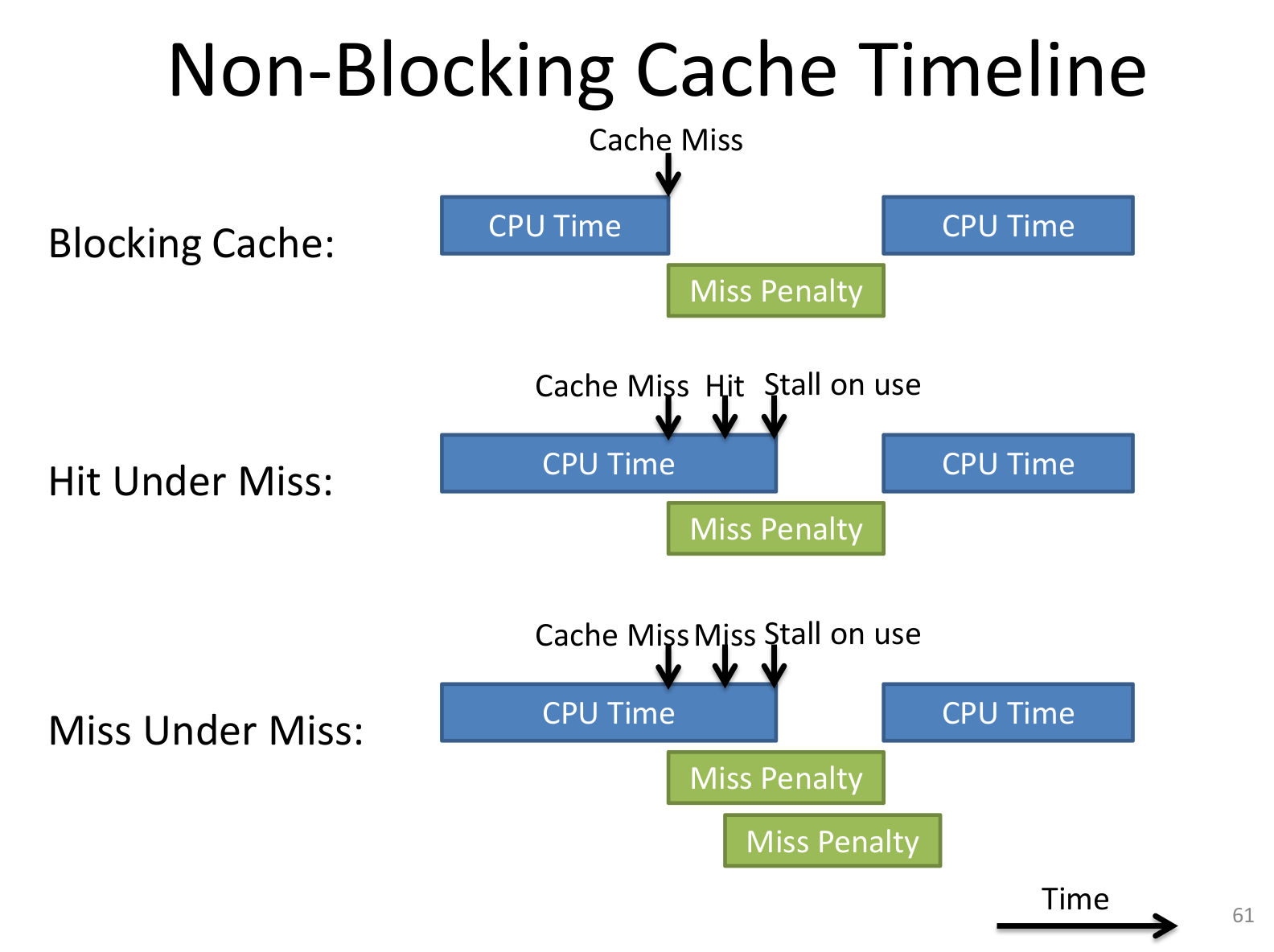
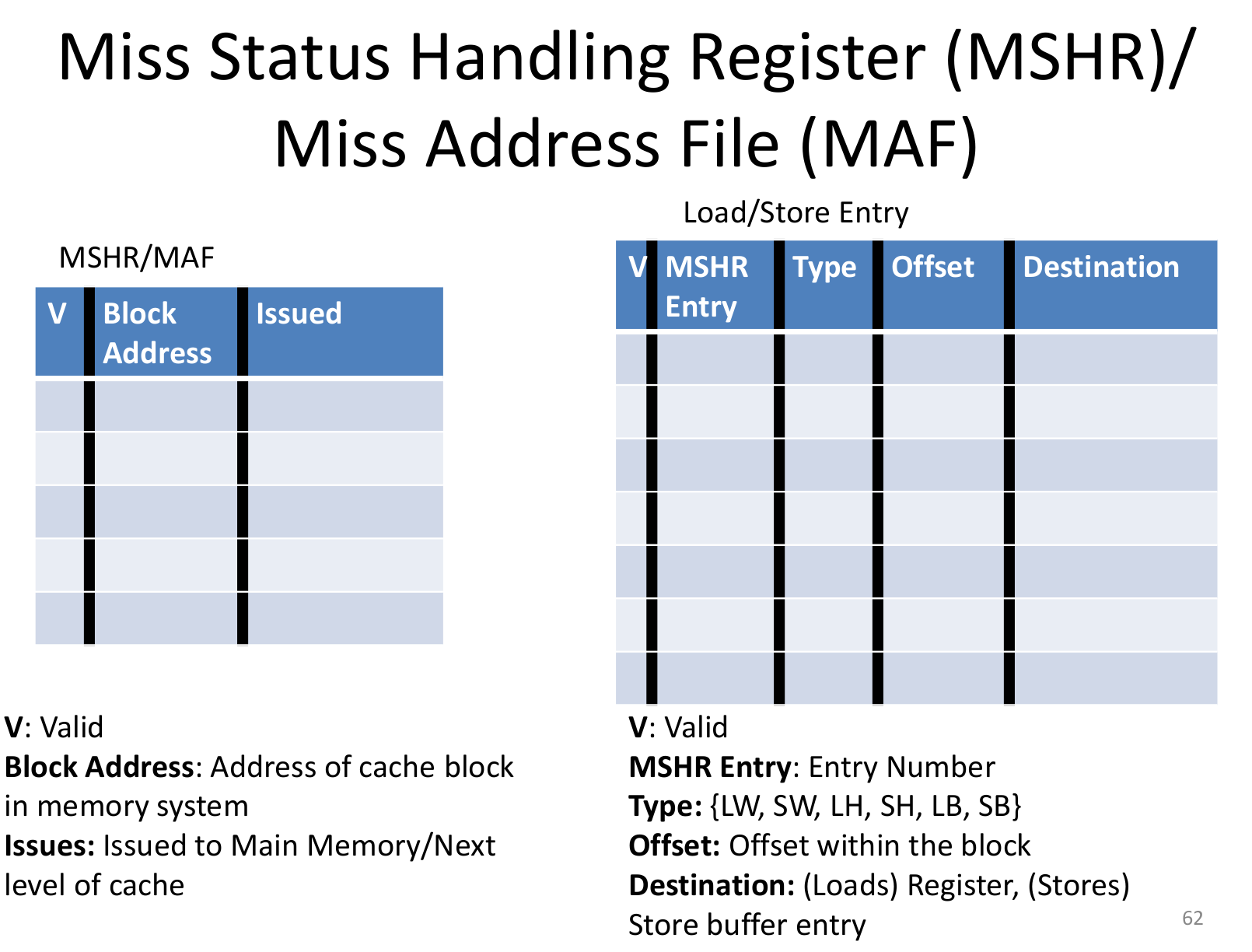
in-order / out-of-order都可以,有一个结构可以记录有哪些cache miss
Critical Word First
Request the missed word from memory first. 相当于指定优先级
early start
不是靠指定优先级先返回,而是返回后立马执行CPU
7. Memory Protection
主要讲页表,跳过
8. Vector Processors and GPUs
Vector Arithmetic Execution 可以使用deep pipeline,这样每个周期的时间更短,且数据间无依赖,没有data hazard,不需要bypassing。
有一套scalar register file,一套vector register file,最基本的vector processor执行,还是每个周期读一个数据
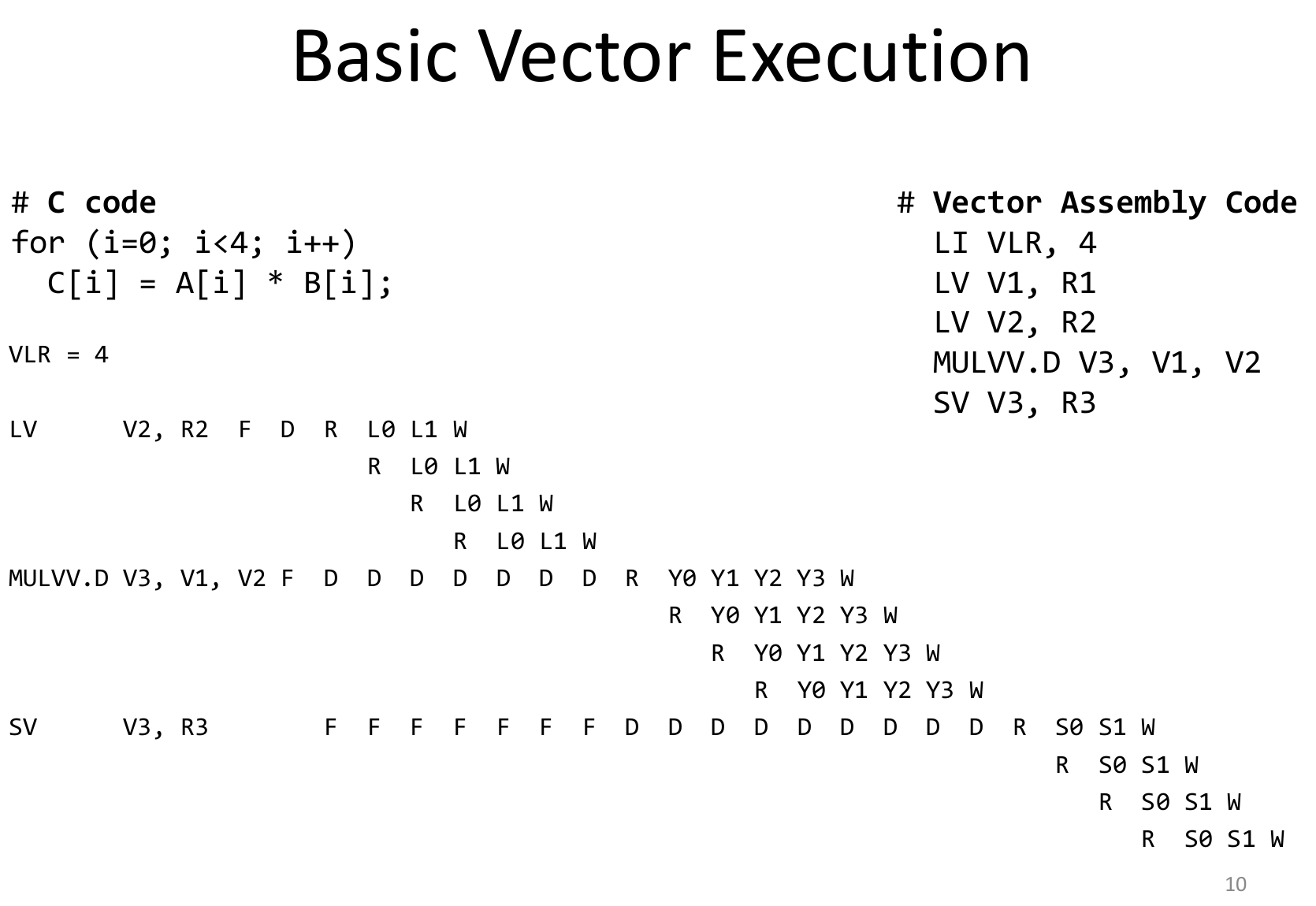
Can overlap execution of multiple vector instructions(Lane)
不懂SIMD/GPU,感觉不是很适合入门,跳过。
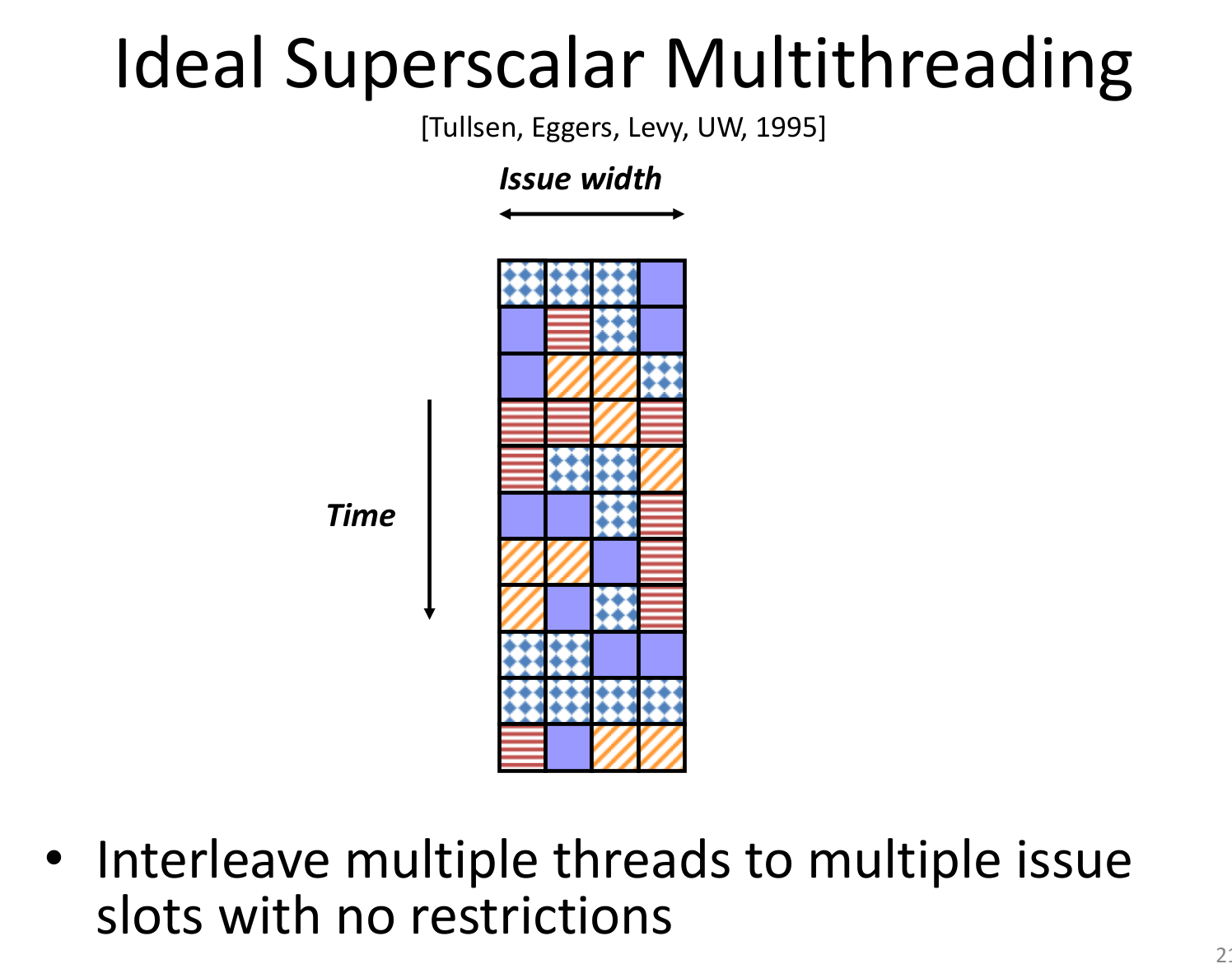
9. Multithreading
这里的 multithreading 不完全是指操作系统那里的线程,而是硬件层面切换执行两个不同的指令流。需要维护多套寄存器,PC等等,但关键是cache,TLB 可能缓存效果变差。那么到底选择哪一个 thread 来执行呢,可以由软件指定优先级,也可以由硬件在遇到阻塞时(比如cache miss)自动切换
Simultaneous Multithreading
非常复杂的结构
奔腾4 超线程,只增加了5% 的die area
- A cache coherence protocol ensures that all writes by one processor are eventually visible to other processors, for one memory address (updates are not lost)
- A memory consistency model gives the rules on when a write by one processor can be observed by a read on another, across different addresses
snoopy cache
- write update(boradcast) 适合读多写少
- write invalidate 目前更常见,消耗带宽少,比如MESI协议
snoopy cache问题主要在于bandwith(核数增多时)
CPU核之间除了 bus 连接通信外,也可以采用message passing的方式,有interconnection network,有点类似于计算机网络,不过是core之间的通信。
cache miss的种类有compulsory, conflict,capacity 和 coherency(为了coherence需要invalid 一些cache block)
总结
前面讲流水线还是比较细节的,但是最后 multiprocessor 部分感觉主要还是介绍概述的多,毕竟没有讲授某种具体的CPU,只是大概介绍了有哪些技术。